
Middleware API - A Smart Alternative to Point-to-Point Integrations?
In the air freight industry, digitalization has become essential for maintaining competitiveness and achieving growth. Optimizing operations is no longer merely an option, but a crucial requirement to remain relevant or even grow your competitive range to adapt to market. When it comes to connecting systems, making the right choice between modern middleware API integrations and traditional point-to-point connections plays a vital role.
What are Point-to-Point Integrations and Middleware API?
Point-to-point integration directly connects two systems to exchange data without an intermediary. It becomes more complex to manage as the number of systems increases because each connection must be established and managed individually.
Middleware API integration acts as a central hub, linking several systems via a single platform. Rather than creating separate connections for each new system, middleware centralizes and simplifies interactions, offering greater scalability and long-term efficiency.
Middleware API solutions offer scalability and flexibility, while point-to-point connections, though more direct and familiar, face significant limitations in terms of adaptability and long-term digital evolution.
Middleware APIs are emerging as the innovative and sustainable solution, revolutionizing the logistics industry by simplifying processes and transforming the way companies interact with their network partners.
Selecting the appropriate integration approach is essential for driving operational efficiency and ensuring success in this increasingly digital landscape.
Overview
The following visual diagram represents the operating circuit of each integration ⇩
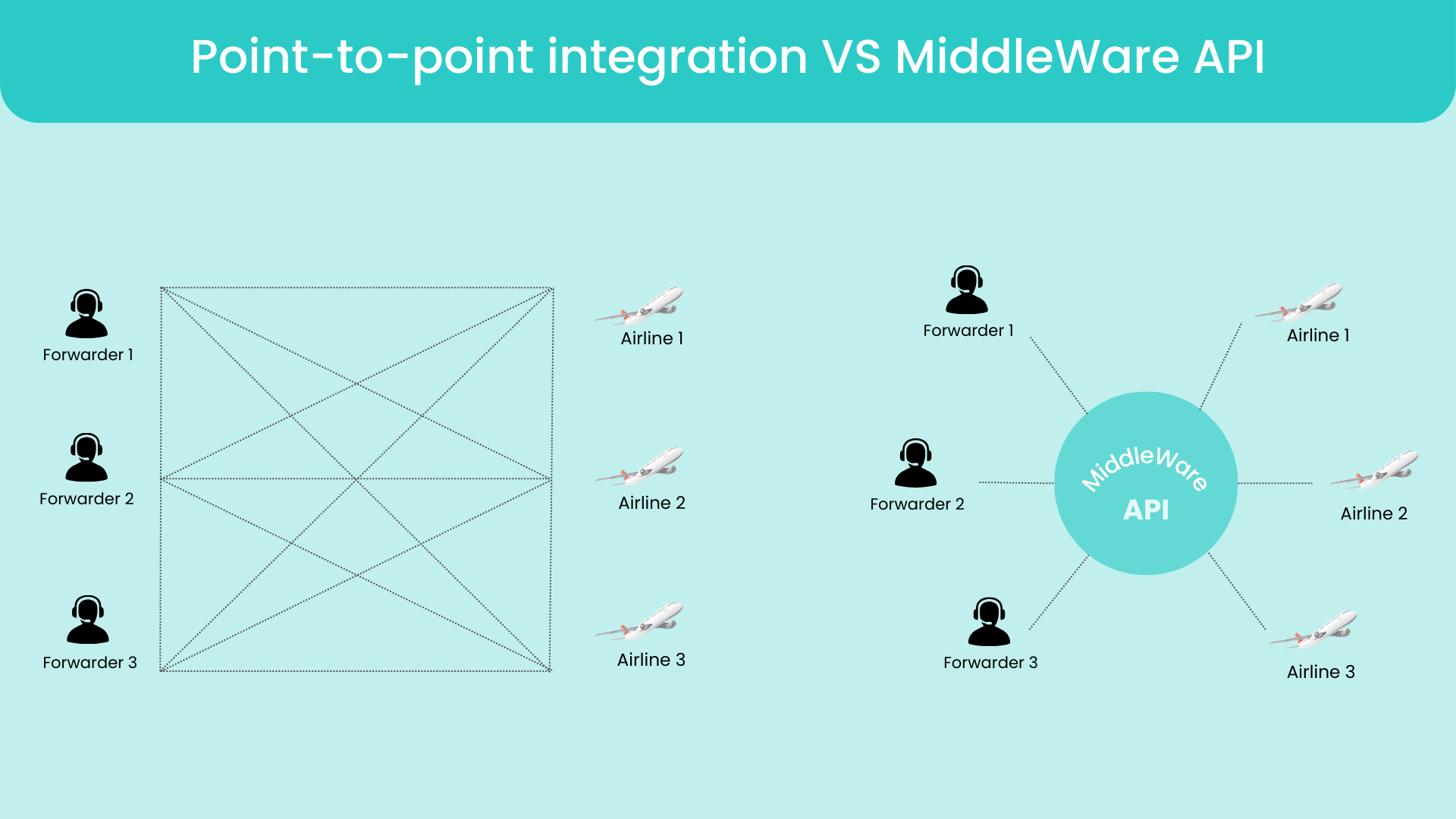
In Point-to-Point Integration each system is directly linked to another to exchange data. This means for each new connection, a specific relationship must be created and managed between the systems. Each system communicates with every other system it needs to interact with to exchange data. For example, if you have three systems (A, B, and C), system A would need to integrate with both B and C separately. This can be straightforward to implement for a small number of systems, and often results in lower latency because they communicate directly with intermediary steps. But with that, as the number of systems grow, the number of connections grows exponentially, which can become complex and difficult to maintain.
Middleware API integration simplifies exchanges by centralizing connections via an intermediary platform. Each system connects to the middleware, which manages exchanges between systems. This reduces the number of connections required and makes it easy to add or modify systems without affecting the others. While this may require an upfront investment for the initial setup and configuration, its reusability and scalability mean simpler management and reduced maintenance or monitoring costs in the long run.
Comparing the two integration strategies
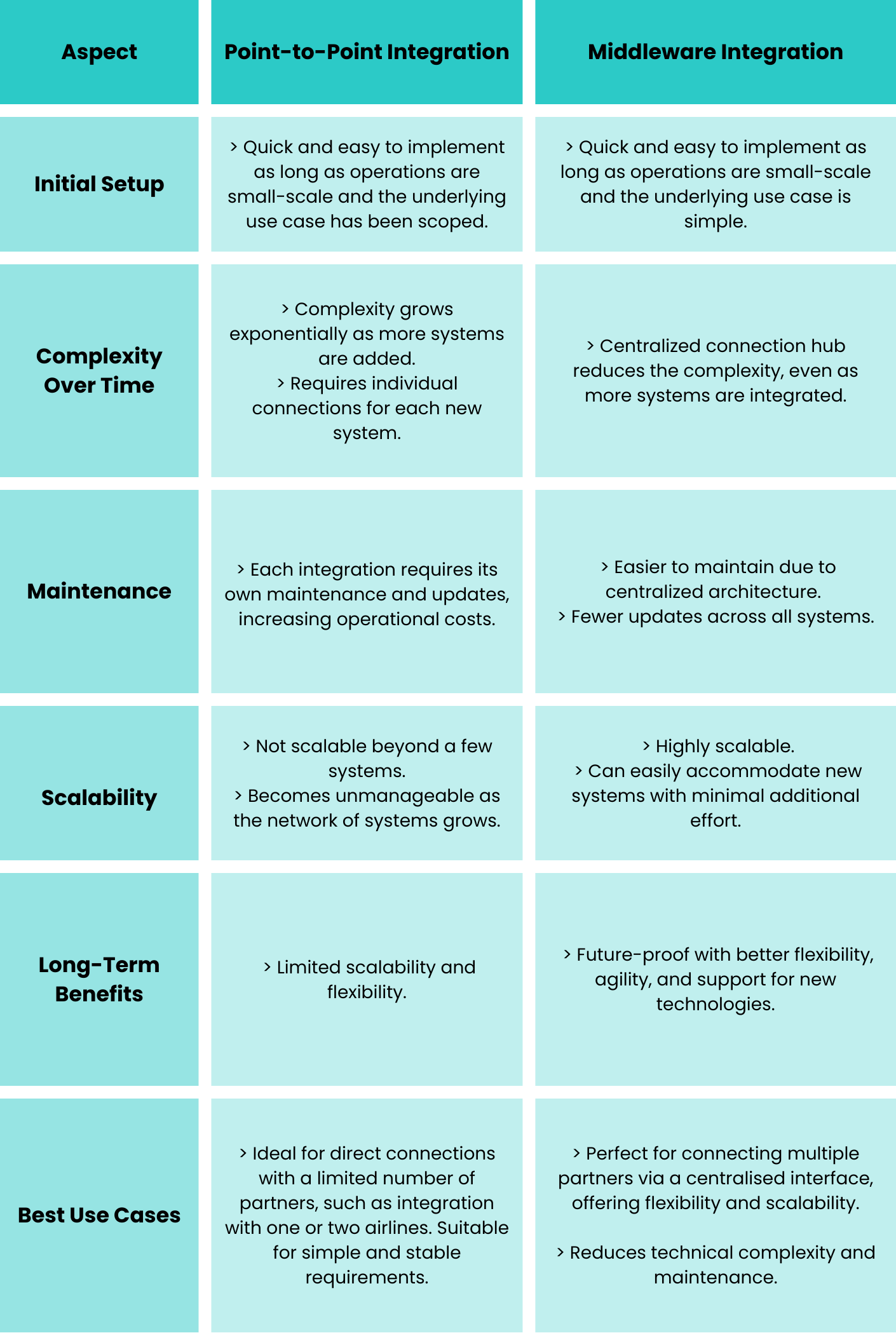
Let's look at some scenarios
Long-term cost
A logistics company integrates directly with several airlines, but each update or modification requires additional technical resources to configure each integration separately, resulting in high recurring costs and a loss of valuable time. In this context, it is crucial to evaluate the initial costs associated with implementing an API middleware. Using such middleware means that updates can be centralized, reducing maintenance costs over the long term and improving the scalability of systems.
Technical expertise vs. core business
A logistics SME, lacking in-house technical resources, is struggling to efficiently integrate with multiple airlines. By adopting a middleware API, the company can delegate the technical integration to a specialized solution partner, allowing for continuous improvement and enabling their team to focus on its core logistics operations. However, it is crucial to ensure that the middleware evolves with customer feedback, allowing the team to concentrate on higher leverage tasks, such as customer service and business expansion instead of spending time resolving issues and troubleshooting.
Speed to Market
A company aims to instantly connect with several airlines, but a point-to-point integration would be very time-consuming to accomplish. By using a middleware API integration, the integration time is significantly reduced, providing more efficient access to a large network of airlines. However, achieving full coverage may still require additional time and resources for airlines that are not immediately integrated into the system.
Network Effect
A company is facing data quality issues with its direct integrations. By adopting a middleware API, errors are quickly identified and corrected through the network effect, leading to improved data exchange quality. However, it is essential to ensure that the network is extensive enough to fully maximize these benefits.
Given that each airline has their own business rules and data sets, integrating them separately into an already complex system would be tedious. By integrating the CargoCONNECT middleware APIs, you can integrate with hundreds of airlines without having to worry about adapting your system to each of the specificities of each API. This will allow you to quickly provide services that meet the daily constraints of your logistics operations.
At CargoAi, innovation is at the heart of our mission. In addition to our revolutionary CargoMART platform, we have built up a team of experts around the world that work on a range of CargoCONNECT APIs based on the middleware API model, to offer our customers maximum flexibility and scalability.
Through our CargoCONNECT APIs, such as the Route & Schedule API, Rate & Book API, Track & Trace API, Cargo2ZERO API, and FWB/FHL API & CargoWALLET API, we enable airfreight companies to easily integrate and automate their logistics operations.
In future blogs, we'll explore in more detail how these APIs are transforming the industry, simplifying processes and optimizing performance.
Would you like more information on how middleware API integrations can benefit you and your business? Don't miss the opportunity to attend a free demo with an expert from the CargoCONNECT team here.
For more information about CargoCONNECT, CargoAi’s API suite, download our brochure or contact our Support team.