
Understanding Latency in Airfreight and how APIs can help reduce it
In the fast-paced world of airfreight, information is as valuable as the cargo itself. Whether you are tracking a critical shipment, booking cargo space on a flight, or planning supply chain management, having timely and accurate data is crucial. This is where APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) come into play, serving as the digital highways that deliver this vital information to your fingertips.
But what happens when these highways experience traffic jams or detours? That is where we encounter the concept of latency – a challenge that can significantly impact your airfreight operations.
In this guide, we will delve into the concept of latency and its implications for you as an airfreight service user. We will discuss how it impacts your operations and what steps you can take to address it. At the conclusion of the blog, you will be well-prepared to navigate the digital landscape of airfreight and make informed decisions for your business.
What is Latency?
Latency is essentially a delay in the transmission of data or information. In the context of airfreight, it is especially important to understand the two types of delays we can face in our day to day:
- System Response Time: This refers to the time lag between when you request information—such as a booking query or tracking update—and when you receive a response. Ideally, this process should occur almost instantaneously, but several factors can cause delays.
- Event Reporting Delay: This is the delay between an event occurring in real-time—such as a plane landing at its destination or a shipment being manifested and loaded—and the corresponding update in the system. For instance, a flight may land at 2:00 PM, but the system might not reflect its actual status as "arrived" until three hours later at 5:00 PM.
Both types of latency can affect your operations, sometimes in different ways. When we talk about API latency, we are often referring to the first type, but as a user, you will likely encounter both.
Latency in Air Freight Shipment Tracking: A Prevalent Challenge
In the world of air freight, shipment tracking is particularly susceptible to latency issues. This prevalence of latency can significantly impact your operations, financials and customer experience.
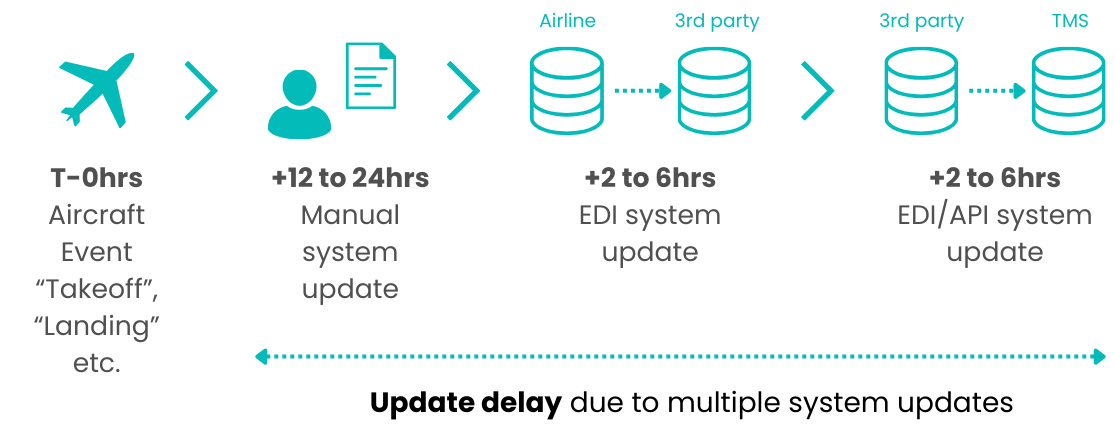
As you advance through each stage of the supply chain, it can create a potential point of delay. Despite increasing advancements in automation and innovation, many tracking updates are still being sent and received via Electronic Data Exchange (EDI). This means that tracking information is often processed in batches, as information is first accumulated and sent at scheduled intervals rather than immediately. EDIs are also typically designed for structured, formal transactions rather than real-time interaction. This can result in significant delays between an event occurring and it being reflected in tracking systems.
As industry standards for timely communication continue to rise, are solution providers prepared? Near real-time updates are essential for building trust, and with freight forwarders now aiming for 95% of event timestamps within a maximum of two to three hours, solution providers are still trying to keep pace.
How Latency Affects Your Airfreight Operations
Latency is not just a technical hiccup – it can have real, tangible impacts on your business:
- Booking and Quotations:
- Slow response times can lead to missed business opportunities. If it takes too long to return a quote or confirm a booking to a customer, you might lose out to a competitor who can move faster.
- Inaccurate or delayed data can lead to overbooking or underutilization of available capacity, impacting profitability.
- Tracking and Visibility:
- Delays in tracking updates can create uncertainty regarding your shipment's status, complicating the planning of downstream operations and making it challenging to keep your customers informed.
- In time-sensitive situations, like cold chain logistics, even a small delay in information could have significant operational and financial consequences.
- Planning and Decision-Making:
- If you are working with outdated information due to latency, it can lead to suboptimal decisions with routing, resource allocation, or customer communications.
- Delays in receiving critical updates, such as flight delays or customs holds can hinder your ability to react quickly and mitigate these issues.
- Customer Service:
- In an age where customers demand immediate access to real-time information, latency in your systems can lead to frustration and a perception of poor customer service.
- If you are relying on lagging data, you might provide inaccurate information to your customers, damaging your trust and reputation.
Understanding these impacts is the first step in managing latency effectively. In the next section, we will explore the common causes of latency in airfreight, giving you insight into why these delays occur and providing you with solutions on how to deal with them.
Common Causes of Latency in Airfreight
To effectively manage latency, it is important to understand where it comes from. Here are some of the most common causes of latency in airfreight systems:
- Delays in Event Recording:
Human Factors: Many events in the airfreight journey still rely on manual input. For example, a ground handler might not immediately update the system when a package is loaded onto a plane.
Batch Processing: Some systems, especially older ones, might update in batches rather than in real-time, causing delays in reporting. - Complex Systems and Data Processing:
Multiple Handoffs: A single shipment might pass through numerous hands – airlines, ground handlers, customs, freight forwarders. Each handoff is a potential point of delay in data updating.
Data Integration: Integrating data from multiple sources, including flight information, customs status, and warehouse operations, requires time and can lead to delays.
- Global Nature of Airfreight:
When you're dealing with global shipments, time zone differences can affect when updates are processed, and each jurisdiction may have its own systems and processes. - Technology Integration:
Legacy Systems: The airfreight industry still relies on many older systems that weren't designed for real-time data exchange. Information sent through these outdated systems can introduce increased latency.
System Overload: During peak times, high volumes of requests can overwhelm systems, leading to slower response times.
Understanding these causes can help you set realistic expectations and work more effectively with your service providers to minimize the impact of latency on your operations. In the next section, we'll compare two main methods of data exchange in airfreight – EDI and API – and how they differ in terms of latency.
EDI vs API: What Users Need to Know
As a user of airfreight services, you might encounter two main methods of exchanging data: Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) for standardized data exchange and APIs.
Understanding the differences between these two can help you make informed decisions about your data needs and set appropriate expectations for latency. We have covered the evolution and basics of these two technologies in our previous introductory blog here.
EDI vs API: Latency Differences
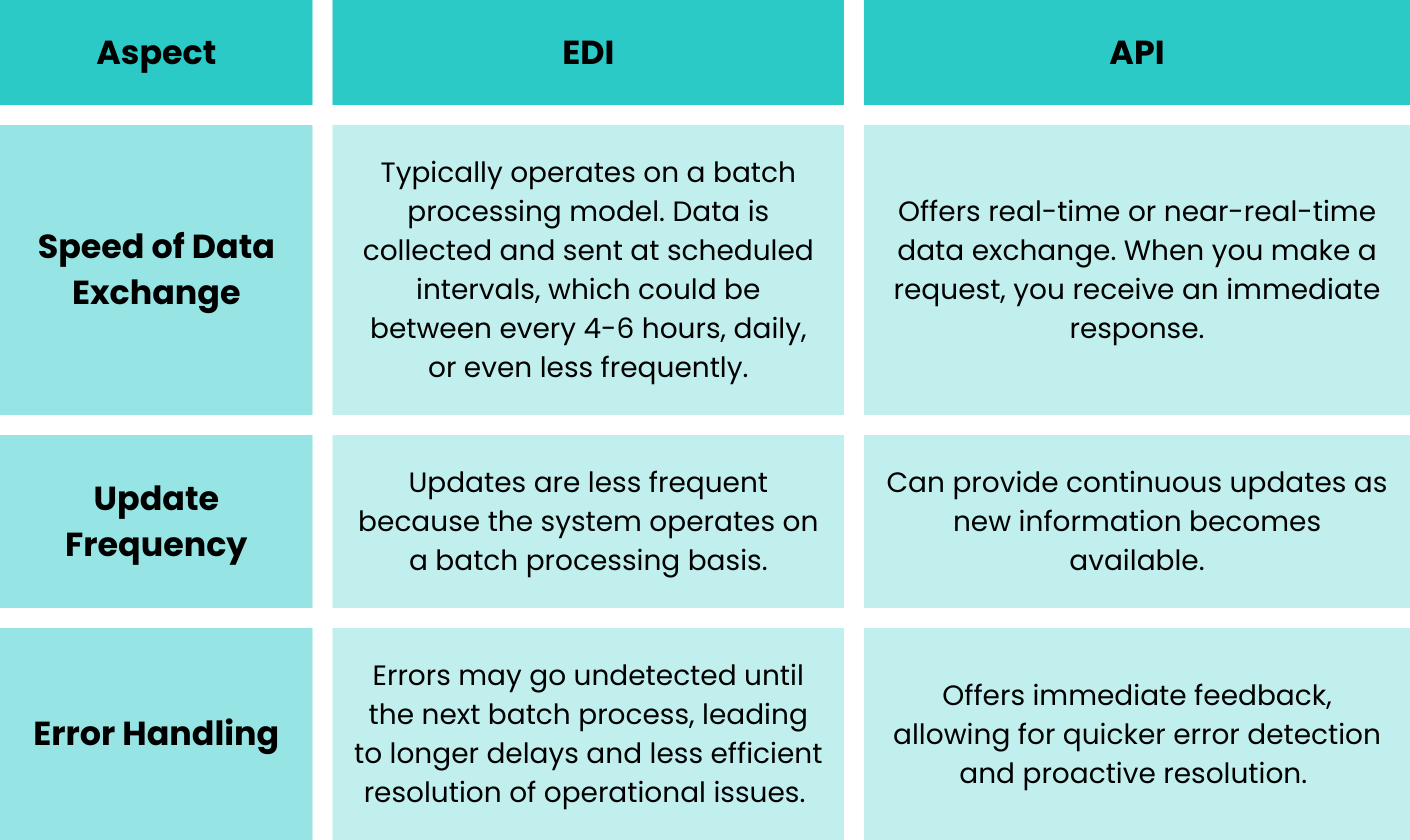
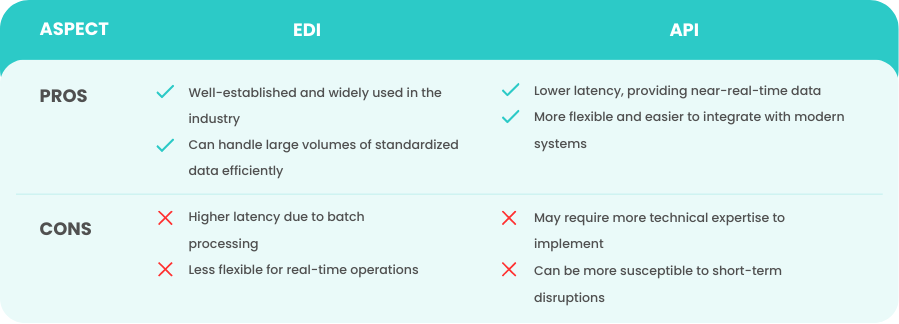
Pros and Cons from a User's Perspective
How Latency Standards Have Changed
The expectations for data speed in airfreight have evolved over the years. Understanding this evolution can help you gauge where the industry is heading and what you should expect from your service providers.
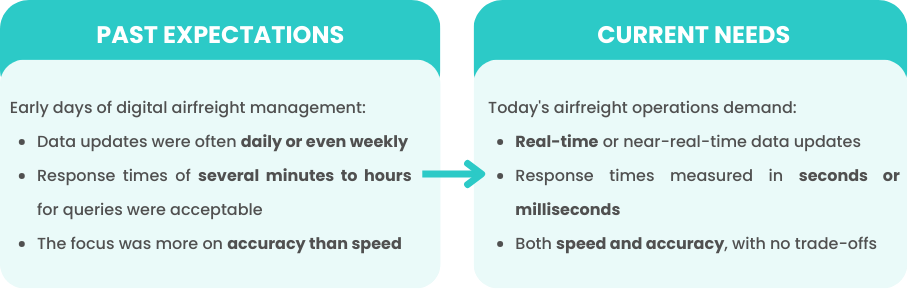
In the past, 6-hour latency was considered acceptable. This allowed for a more relaxed approach and provided sufficient time for logistical adjustments. Nowadays, customers are increasingly demanding more frequent updates. As such, a 2-hour latency window has become a common benchmark.
Looking ahead, the expectation is that tracking information will need to be updated within a 1-hour window. This is influenced by increased consumer expectations, the need for a competitive advantage, and sustainability goals.
Factors Driving the Demand for Faster Data
- E-commerce Growth: The boom in e-commerce has led to increased expectations for fast shipping and real-time tracking.
- Just-in-Time Manufacturing: Many industries now operate on lean inventories, requiring precise timing of shipments.
- Global Competition: In a highly competitive market, faster data can provide a significant edge.
- Customer Expectations: In an age of instant information, customers expect immediate answers about their shipments.
- Risk Management: Faster data allows for quicker responses to disruptions, minimizing their impact.
Dealing with Latency
While you can't eliminate latency entirely, there are strategies you can employ to minimize its impact on your operations. Here are some practical tips:
- Understand Realistic Expectations: Know the current industry standards for different types of data updates. Recognize that some latency is inevitable, especially for complex, global operations.
- Implement Local Caching: For frequently accessed, relatively static data (like general flight schedules), consider caching the information locally to reduce response times. Ensure you have a strategy to update this cached data regularly.
- Plan for Latency: Build buffer time into your processes to account for potential delays in data updates. Have contingency plans for situations where critical data might be delayed.
- Leverage Predictive Analytics: Use historical data and AI to predict likely outcomes when real-time data is delayed. This can help you make informed decisions even when facing latency issues.
- Educate Your Team: Ensure your staff understands the realities of data latency in airfreight. Train them on how to make decisions and communicate with customers when facing delays in data updates.
By implementing these strategies, you can better manage the impact of latency on your airfreight operations. Remember, the goal isn't to eliminate latency entirely, but to understand it, plan for it, and minimize its impact on your business.
Setting New Standards for Shipment Tracking: CargoAi's Track and Trace API
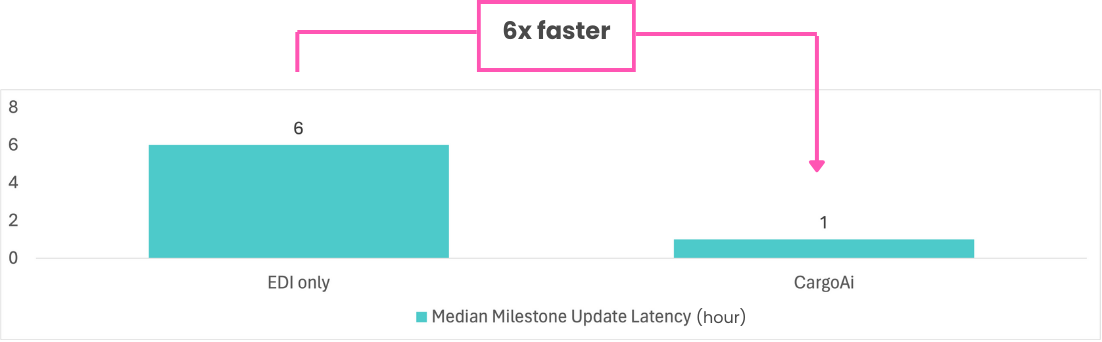
Cargoai’s Track and Trace solution has some of the best latency standards in the industry. Through our unique Track and Trace API we provide access to and visibility of the largest airline and GHA portfolio in the air freight industry. We also combine multiple sources to retrieve data, so that you and your customers will be the first ones notified of any updates or changes in shipment statuses/milestones.
Our Track and Trace solution is designed to provide timely updates with a guaranteed latency of less than two hours from the time an event is published by the airline. To learn more about our latency results you can view our latency dashboard.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing latency is crucial for anyone involved in airfreight operations. As we've explored in this guide, latency isn't just a technical issue – it has real, tangible impacts on your business, from affecting your ability to make timely decisions to influencing customer satisfaction.
The key is to understand these delays, plan for them, and develop strategies to work effectively within the realities of global airfreight operations.
Stay tuned for our next week's blogs that will deep dive into a few key API use cases.
For more information about CargoCONNECT, CargoAi’s API suite, download our brochure or contact our Support team.